Introduction
Imagine you’re working on a computer, and instead of saving files or programs on your device, everything is stored and accessed through the internet. That’s the power of cloud computing.
In today’s world, we use the cloud without even realizing it — when we watch movies on Netflix, save photos on Google Drive, or check emails on Gmail.
But what exactly is cloud computing, how does it work, and why is it so important?
This article explains everything about cloud computing in very simple and easy words, including its meaning, types, advantages, and real-life examples.
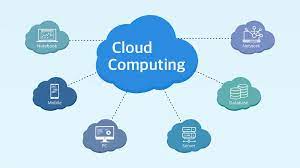
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing means using the internet to store, manage, and process data instead of using your own computer or hard drive.
In simple terms:
Cloud computing = Using someone else’s computer (on the internet) to do your work or store your data.
The “cloud” refers to remote servers that are hosted on the internet. These servers store your files, run applications, and provide services — all available anytime, anywhere.
Example:
When you upload photos to Google Photos, your data is stored on Google’s cloud servers — not on your phone.
When you use Microsoft Word Online, the software runs on the cloud, not on your local device.
How Cloud Computing Works
Cloud computing works by connecting your device (like a phone or laptop) to remote servers through the internet.
Here’s how it works step by step:
- You open an app or website that uses cloud computing (like Google Drive).
- You upload or access data.
- That data is sent through the internet to powerful servers in data centers.
- The servers process, store, or deliver your data back to you.
- You can access your files or apps anytime, from any device.
These servers are managed by cloud companies such as Amazon (AWS), Microsoft (Azure), Google (GCP), and IBM Cloud.
Main Features of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers several useful features that make it powerful and flexible:
- On-Demand Access:
You can use services whenever you need them. - Scalability:
You can easily increase or decrease storage or computing power. - Accessibility:
Access your data or applications from anywhere using the internet. - Automatic Updates:
Cloud providers keep everything updated and secure. - Pay-as-You-Go:
You only pay for what you use — like paying for electricity or water.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is divided into three main service models, based on what kind of service is offered.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides basic computing infrastructure like virtual machines, storage, and networks over the internet.
Examples:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Compute Engine
- Microsoft Azure
Use case:
Companies use IaaS to host websites or store large amounts of data without buying physical servers.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform for developers to build and deploy applications without worrying about managing servers.
Examples:
- Google App Engine
- Heroku
- Microsoft Azure App Service
Use case:
Developers use PaaS to create web or mobile apps quickly.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet. Users don’t need to install anything — they can access the software using a browser.
Examples:
- Gmail
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Office 365
- Zoom
- Dropbox
Use case:
People use SaaS daily for email, file sharing, meetings, and office work.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud computing can also be divided based on how it’s used or owned.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Services shared by many users through the internet. | Google Cloud, AWS |
| Private Cloud | Used by a single organization for better control and security. | Banking or government clouds |
| Hybrid Cloud | A mix of public and private clouds. | IBM Hybrid Cloud |
| Community Cloud | Shared by several organizations with similar needs. | Universities or hospitals sharing a common cloud |
Each model has its own benefits depending on the user’s needs.
Examples of Cloud Computing in Daily Life
You probably use cloud computing several times a day without realizing it:
| Service Type | Example | How It Uses the Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| File Storage | Google Drive, Dropbox | Save and access files online |
| Streaming | Netflix, YouTube, Spotify | Watch or listen without downloading |
| Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo Mail | Send and receive emails anywhere | |
| Collaboration | Google Docs, Microsoft Teams | Work with others in real time |
| Social Media | Facebook, Instagram | Share photos and videos |
| Online Backup | iCloud, OneDrive | Store important data securely |
So, cloud computing makes modern life more connected and convenient.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has changed the way we use technology. Here are some major benefits:
1. Cost-Effective
You don’t need to buy expensive computers or servers. You pay only for what you use.
2. Accessibility
You can access your files, apps, or tools from anywhere in the world using the internet.
3. Scalability
Easily increase or decrease resources based on your needs — useful for growing businesses.
4. Automatic Updates
Cloud service providers handle maintenance and updates automatically.
5. Data Backup and Recovery
Your files are safely stored, and you can recover them even if your device breaks.
6. Collaboration
Multiple people can work together on the same project in real time.
7. Security
Most cloud providers use strong encryption and security measures to protect data.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
While cloud computing offers many advantages, it also has some challenges:
1. Internet Dependency
You need a stable internet connection to use cloud services.
2. Data Privacy
Your data is stored on third-party servers, which can raise privacy concerns.
3. Downtime
If the cloud service goes down, users can’t access data or apps.
4. Limited Control
Users rely on providers for maintenance and updates.
5. Hidden Costs
Some cloud services can become expensive over time with high usage.
Despite these drawbacks, most people and businesses find cloud computing highly reliable and cost-effective.
Who Uses Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is used by almost every type of user:
| User Type | Example Uses |
|---|---|
| Individuals | Storing photos, streaming movies, checking email |
| Small Businesses | Managing data, accounting, and customer communication |
| Large Companies | Hosting applications, analyzing data, managing servers |
| Government Organizations | Storing public records securely |
| Schools and Universities | Online learning, student portals, and file sharing |
So, whether for personal or professional use, the cloud is everywhere.
Cloud Computing Security
Security is one of the most important parts of cloud computing. Providers use several methods to keep your data safe:
- Encryption: Converts your data into unreadable code during transfer.
- Firewalls: Block unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Adds extra login security.
- Data Backups: Keeps copies of your files in multiple locations.
- Regular Updates: Fix security bugs and weaknesses.
You can also keep your data safe by using strong passwords and enabling two-step verification.
Real-Life Examples of Cloud Providers
Here are some of the biggest cloud computing platforms:
| Company | Cloud Service Name | Main Features |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon | Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Largest cloud platform, offers IaaS & PaaS |
| Microsoft | Azure | Integrates well with Windows & Office |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Great for AI and data analytics | |
| IBM | IBM Cloud | Focuses on enterprise and AI |
| Oracle | Oracle Cloud | Known for database services |
These companies manage millions of servers and store data for people and businesses around the world.
Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing continues to grow and evolve every year. In the future, it will become even more intelligent, faster, and more secure.
Upcoming trends:
- AI and Machine Learning in Cloud: Smart systems that automate tasks.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to where it’s created for faster results.
- Hybrid Clouds: Combining private and public clouds for flexibility.
- Serverless Computing: Running apps without managing any servers.
- Green Cloud Computing: Reducing energy use and protecting the environment.
The future cloud will power smart homes, businesses, robots, and even cities.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has completely changed how we use and store data. It lets people and organizations work faster, save money, and access powerful technology from anywhere in the world.
From checking your email to managing entire businesses, the cloud is everywhere. It has made technology more flexible, affordable, and available to everyone.
In simple words:
Cloud computing means freedom — the power to access anything, anytime, from anywhere.
As the world becomes more digital, cloud computing will continue to grow — shaping the future of technology, business, and communication.